HWA Tutorial On NVIDIA GPU
This tutorial guides you on setting up full video hardware acceleration on NVIDIA GPU via NVENC.
Acceleration Methods
Hardware accelerated transcoding is supported on NVIDIA GPUs since Maxwell architecture.
On Windows and Linux NVENC is the only available method.
The NVENC/NVDEC are the proprietary video codec APIs of NVIDIA GPUs, which can be used with CUDA to achieve full hardware acceleration.
Please refer to this section for known issues and limitations.
NVENC supports headless server on both Windows and Linux, which means a connected monitor is not required.
Tone-mapping Methods
Hardware accelerated HDR/DV to SDR tone-mapping is supported on all NVIDIA GPUs that have HEVC 10-bit decoding.
On Windows and Linux CUDA is the only available tone-mapping method. It also supports Dolby Vision P5 and zero-copy.
The Enable enhanced NVDEC decoder feature toggles between the newer NVDEC and the older CUVID decoding processes. Dolby Vision support requires that this option be checked in order to enable NVDEC.
Select GPU Hardware
For beginners, please refer to the Hardware Selection Guide for tips on selecting hardware. For expert users, please continue reading this section.
Most NVIDIA GPUs come with NVENC/NVDEC support but some low-end and mobile models (e.g. GT1030 and MX450) are exceptions.
Video codec support can be checked via the NVIDIA GPU Codec Support Matrix prior to buying a GPU suitable for hardware acceleration.
Transcode H.264
AVC / H.264 8-bit is still widely used due to its excellent compatibility. All NVIDIA GPUs supporting NVENC/NVDEC can decode and/or encode it.
- Decoding & Encoding H.264 8-bit - Any NVIDIA GPU supporting NVENC/NVDEC
Transcode HEVC
HEVC / H.265 remains the first choice for storing 4K 10-bit, HDR and Dolby Vision video. It has mature software encoding support thanks to x265, as well as the widely implemented hardware encoding support in most GPUs released after 2016.
Maxwell+ GPUs provide support for HEVC:
-
Decoding & Encoding HEVC 8-bit - Maxwell 2nd Gen (GM206) and newer
-
Decoding HEVC 10-bit - Maxwell 2nd Gen (GM206) and newer
-
Encoding HEVC 10-bit - Pascal and newer
Note that in Maxwell 2nd Gen series only the GM206 variants provide HEVC 10-bit decoding support. Its sucessor Pascal has full support for HEVC 10-bit and improved speed and quality.
Transcode AV1
AV1 is a royalty-free, future-proof video codec. It saves a lot of storage space and network bandwidth due to smaller file size. The downside is that decoding and encoding is very demanding on the CPU. Hardware acceleration makes it possible to transcode AV1 streams on the fly. AV1 encoding is supported in Jellyfin 10.9 and newer.
NVIDIA added support for AV1 acceleration in their latest GPUs:
-
Decoding AV1 8/10-bit - Ampere and newer
-
Encoding AV1 8/10-bit - Ada Lovelace and newer
Transcode Other Codecs
Please refer to these links:
Speed And Quality
Encoding quality:
-
H.264 & HEVC - Ada/Ampere/Turing > Turing TU117/Volta/Pascal > Maxwell
-
AV1 - Ada Lovelace only
Decoding & Encoding speed within the same generation:
-
Multiple NVENC/NVDEC models > Single NVENC/NVDEC models
-
High GPU clock speed models > Low GPU clock speed models
-
High memory bandwidth models > Low memory bandwidth models
NVENC/NVDEC performance tables:
Windows Setups
Windows 10 64-bit and newer is recommeded. In Jellyfin 10.10 the minimum required NVIDIA driver version is 522.25.
Configure On Windows Host
-
Wipe the old driver with DDU if you upgraded from a pre-Maxwell NVIDIA GPU without doing a fresh installation.
-
Clean install the latest driver from NVIDIA Driver Downloads.
-
Enable NVENC in Jellyfin and uncheck the unsupported codecs.
Configure With Windows Virtualization
NVIDIA Windows driver provides access to the NVENC/NVDEC and CUDA in Windows WSL2 and Docker.
Refer to Configure On Linux Host and Configure With Linux Virtualization.
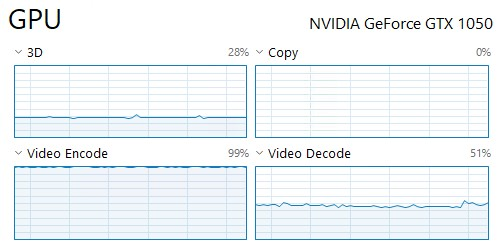
Verify On Windows
-
Play a video in the Jellyfin web client and trigger a video transcoding by setting a lower resolution or bitrate.
-
Open the "Task Manager" and navigate to the GPU page.
-
Check the occupancy of the engines as follows.
-
3D - 2D/3D engine or CUDA/GPGPU workload
-
Copy - Blitter/Copy engine workload
-
Video Decode - Video decoder workload
-
Video Encode - Video encoder workload
-
Cuda - CUDA/GPGPU workload
-
Linux Setups
A 64-bit Linux distribution is required. In Jellyfin 10.10 the minimum required NVIDIA driver version is 520.56.06.
Configure On Linux Host
Debian And Ubuntu Linux
The jellyfin-ffmpeg* deb package required by Jellyfin doesn't include any NVIDIA proprietary driver.
You have to install the NVIDIA driver from the distro and configure the permission of the jellyfin user.
Root permission is required.
-
Assuming you have added the jellyfin repository to your apt source list and installed the
jellyfin-serverandjellyfin-web. -
Install the
jellyfin-ffmpeg7package. Remove the deprecatedjellyfinmeta package if it breaks the dependencies:sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y jellyfin-ffmpeg7 -
Install the NVIDIA proprietary driver by following these links. Then install two extra packages for NVENC and NVDEC support:
-
On Debian: https://wiki.debian.org/NvidiaGraphicsDrivers
sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y libnvcuvid1 libnvidia-encode1 -
On Ubuntu: https://ubuntu.com/server/docs/nvidia-drivers-installation
noteYou may need to add the driver version as the suffix of the package name.
sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y libnvidia-decode libnvidia-encode
-
-
Check the NVIDIA GPU status by using
nvidia-smi:$ nvidia-smi
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| NVIDIA-SMI 520.56.06 Driver Version: 520.56.06 CUDA Version: 11.8 |
|-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
| GPU Name Persistence-M| Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC |
| Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap| Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. |
| | | MIG M. |
|===============================+======================+======================|
| 0 NVIDIA GeForce ... Off | 00000000:1C:00.0 Off | N/A |
| 0% 44C P0 N/A / 75W | 0MiB / 1998MiB | 0% Default |
| | | N/A |
+-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
... -
Enable NVENC in Jellyfin and uncheck the unsupported codecs.
Linux Mint
Linux Mint uses Ubuntu as its package base.
You can follow the configuration steps of Debian and Ubuntu Linux but install all Jellyfin packages jellyfin-server, jellyfin-web and jellyfin-ffmpeg7 manually from the Jellyfin Server Releases Page. Also make sure you choose the correct codename by following the official version maps.
Arch Linux
Root permission is required.
-
Install the Archlinux/extra
jellyfin-ffmpegpackage:sudo pacman -Syu jellyfin-ffmpeg -
Install the NVIDIA proprietary driver by following the link. Then install an extra package for NVENC and NVDEC support:
sudo pacman -Syu nvidia-utils -
Check the NVIDIA GPU status by using
nvidia-smi:nvidia-smi -
Enable NVENC in Jellyfin and uncheck the unsupported codecs.
Other Distros
We provide portable jellyfin-ffmpeg binaries for distros that don't have a regular maintainer.
They can be downloaded from one of these links:
Minimum requirements for glibc and Linux versions:
- x86_64 / amd64 - glibc >= 2.28, Linux >= 4.18 (most distros released in 2018 and later)
Extract and install it to the correct path, change the FFmpeg path in the Jellyfin dashboard to match it:
Root permission is required.
cd ~/
mkdir -p jellyfin-ffmpeg
wget https://repo.jellyfin.org/releases/ffmpeg/<VERSION>/jellyfin-ffmpeg_<VERSION>_portable_linux64-gpl.tar.xz
tar -xvf jellyfin-ffmpeg_<VERSION>_portable_linux64-gpl.tar.xz -C jellyfin-ffmpeg
sudo mv jellyfin-ffmpeg /usr/lib
sudo ldd -v /usr/lib/jellyfin-ffmpeg/ffmpeg
Install the NVIDIA proprietary driver packages and their dependencies that contain these key words:
-
NVIDIA NVDEC CUVID - DECODE
-
NVIDIA NVENC - ENCODE
Configure With Linux Virtualization
Official Docker
The official Docker image doesn't include any NVIDIA proprietary driver.
You have to install the NVIDIA driver and NVIDIA Container Toolkit on the host system to allow Docker access to your GPU.
Root permission is required.
-
Install the NVIDIA proprietary driver on the host system. See above instructions.
-
Install the NVIDIA Container Toolkit on the host system by following this link:
-
Use the Docker command line or docker-compose:
-
Example command line:
docker run -d \
--name=jellyfin \
--volume /path/to/config:/config \
--volume /path/to/cache:/cache \
--volume /path/to/media:/media \
--user 1000:1000 \
--net=host \
--restart=unless-stopped \
--runtime=nvidia \
--gpus all \
jellyfin/jellyfin -
Example docker-compose configuration file written in YAML:
services:
jellyfin:
image: jellyfin/jellyfin
user: 1000:1000
network_mode: 'host'
volumes:
- /path/to/config:/config
- /path/to/cache:/cache
- /path/to/media:/media
runtime: nvidia
deploy:
resources:
reservations:
devices:
- driver: nvidia
count: all
capabilities: [gpu]
noteIf you encounter the upsteam issue
CUDA_ERROR_NO_DEVICE: no CUDA-capable device is detected, pass these extra devices to the Docker:/dev/nvidia-caps:/dev/nvidia-caps
/dev/nvidia0:/dev/nvidia0
/dev/nvidiactl:/dev/nvidiactl
/dev/nvidia-modeset:/dev/nvidia-modeset
/dev/nvidia-uvm:/dev/nvidia-uvm
/dev/nvidia-uvm-tools:/dev/nvidia-uvm-tools -
-
Add your username to the video group:
sudo usermod -aG video $USER -
Update dynamic links and restart the Docker service:
docker exec -it jellyfin ldconfig
sudo systemctl restart docker -
Check the NVIDIA GPU's status by using
nvidia-smi:docker exec -it jellyfin nvidia-smi -
For trying out the unstable build, change
jellyfin/jellyfintojellyfin/jellyfin:unstableon your own risk. -
Enable NVENC in Jellyfin and uncheck the unsupported codecs.
Note that the official Jellyfin Docker image already sets the required environment variables for NVIDIA GPUs. If you are building your own image don't forget the add two extra environment variables into the Docker configs.
-
NVIDIA_DRIVER_CAPABILITIES=all -
NVIDIA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=all
Linuxserver.io Docker
LSIO Docker images are maintained by linuxserver.io, please refer their docs from GitHub - linuxserver/docker-jellyfin.
The paths of Jellyfin config and data folders in the official and LSIO Docker images are different. So they cannot be easily exchanged.
Other Virtualizations
Other Virtualizations are not verified and may or may not work on NVIDIA GPU.
Refer to the HWA Tutorial On Intel GPU - Configure With Linux Virtualization for more information.
Verify On Linux
-
Play a video in the Jellyfin web client and trigger a video transcoding by setting a lower resolution or bitrate.
-
Use
nvidia-smicommand to check the occupancy of the NVIDIA GPU and the VRAM usage of each jellyfin-ffmpeg process:$ nvidia-smi
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| NVIDIA-SMI 520.56.06 Driver Version: 520.56.06 CUDA Version: 11.8 |
|-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
| GPU Name Persistence-M| Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC |
| Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap| Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. |
| | | MIG M. |
|===============================+======================+======================|
| 0 NVIDIA GeForce ... Off | 00000000:1C:00.0 Off | N/A |
| 43% 44C P2 36W / 75W | 274MiB / 1998MiB | 68% Default |
| | | N/A |
+-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Processes: |
| GPU GI CI PID Type Process name GPU Memory |
| ID ID Usage |
|=============================================================================|
| 0 N/A N/A 4024 G /usr/lib/xorg/Xorg 63MiB |
| 0 N/A N/A 5837 C /usr/lib/jellyfin-ffmpeg/ffmpeg 195MiB |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+