TrueNAS SCALE
Jellyfin can be installed on iX-systems' TrueNAS SCALE.
This document is written for TrueNAS SCALE v24.10.0 (Electric Eel) or higher.
Consider reviewing the TrueNAS Apps documentation if you have not previously configured applications on your system.
- Note: TrueNAS CORE and TrueNAS SCALE are different. Jellyfin is not supported on TrueNAS CORE.
Introduction and Preparation
TrueNAS SCALE lets you run apps using Docker.
There are two supported methods of installing Jellyfin on your TrueNAS SCALE server:
- Custom App
- Community 3rd Party App provided by ix-systems
Both methods use the official Jellyfin-provided Docker image. This document will cover both install methods.
You can configure environment variables at any time after deploying the application.
It is recommend to set the TrueNAS SCALE App system to a storage pool comprised of SSDs.
Datasets & Jellyfin
The official Jellyfin Docker image internally creates the following necessary directories:
- cache
- config
- cache/transcodes
If you use the community app, you can allow SCALE to create datasets for the directories Jellyfin requires automatically during app installation. You can also choose to create a static transcodes dataset or use temporary storage on the disk or in memory (system RAM) for transcoding.
- Note that using RAM for transcodes can be a bad idea as transcodes can take up a lot of space. If there isn't enough memory available in RAM for a transcode, the transcode will fail. It is recommended that you place the transcode directory on a drive with a decent amount of free space to avoid this issue. Consider using an SSD instead of an HDD to avoid possible slowdowns.
You can also create your own custom datasets to use in the Storage Configuration section as host paths during installation.
You can organize datasets as one parent with two child datasets, for example /mnt/tank/jellyfin/config, /mnt/tank/jellyfin/cache, and so on.
With Docker, you can organize these in any way as long as you mount them under the correct name to the Docker container.
It is recommended to set Jellyfin's config directory to an accessible dataset. This will make it easy to backup/restore your server.
It is also recommended to use datasets located on an SSD Storage Pool for Jellyfin's configuration and cache data.
Users & Permissions
You can set the user and group that will run your container when setting up Jellyfin. If you want to run the application with a user or group other than the default apps (568) user and group, create them now.
Make sure your datasets have appropriate permissions set to allow the Jellyfin container user to access your datasets.
Installing as a Custom App
Using YAML
Go to SCALE's Apps section.

Click on the Discover Apps button on the top-right of the page. It will bring you to the community app store.
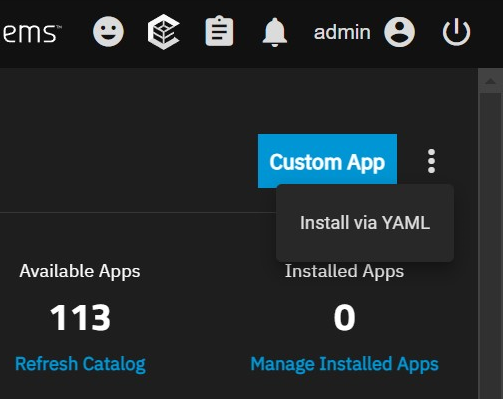
There, click on the 3-dot menu on the top-right and then on Install via YAML.
- Note that you can also install a custom app using SCALE's guided app launcher GUI. Refer to the steps on installing the community app since the layout is largely the same.
- If you go this route, your final Jellyfin container will only be editable through this GUI. If you want access to the Compose YAML editor afterwards, you need to launch your container with the YAML option.
- You will need to pull Jellyfin's image onto your SCALE server depending on the setting you choose on the guided GUI.
- For the Repository field, simply enter
jellyfin/jellyfin. You then specify what Tag (version) you want to pull from the Docker Hub. - See this for more info on container images on SCALE
- For the Repository field, simply enter
A tab will open from the right side of the page where you launch your custom app using a Docker Compose file.
Compose YAML File
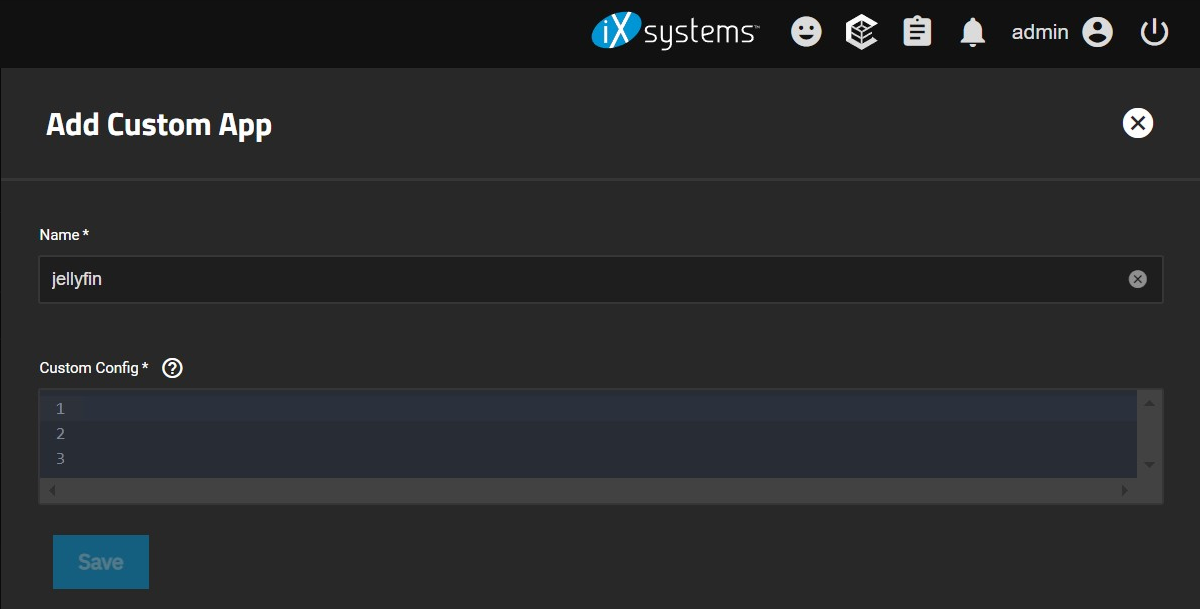
Here, give the custom app a name and write/paste the lines for your compose file.
See here for documentation on using Docker Compose with Jellyfin. Alternatively, here's a basic compose file where you should edit the volumes to use on your system, then copy & paste it into the editor to launch Jellyfin:
services:
jellyfin:
container_name: jellyfin
image: ghcr.io/jellyfin/jellyfin:latest
user: '568:568'
# group_add:
# - '107'
# devices:
# - /dev/dri/renderD128:/dev/dri/renderD128
# - /dev/dri/card0:/dev/dri/card0
environment:
- TZ=America/Los_Angeles
network_mode: bridge
ports:
- 8096:8096/tcp
# cpus: '8' # optional
# mem_limit: 16G # optional
restart: unless-stopped
volumes:
- /mnt/path/to/config:/config:rw
- /mnt/path/to/cache:/cache:rw
# rw = read & write
# ro = read only
- Remember to add your media datasets as extra volumes on your compose file so that the container can access them.
- The user & group you set are only to run the container. They are not used to create a Jellyfin account.
- Make sure your spacing is correct for each option. Compose files use spacing to parse the options correctly.
- You can determine the time zone identifier for you region here.
- Note that lines with
#in front indicate a comment. They will not apply until you remove it. - Uncomment the
group_addanddevicesoptions if you have a GPU and want to use hardware acceleration.- If you have an NVIDIA GPU, please read this.
- Unless you set the container to run as root, you need to add the render group ID to the container with
group_add. - In case the render group's ID is not
107on all SCALE servers by default, go to your system shell and run the following command to get your render group's ID:cat /etc/group | grep render
- Jellyfin's auto discovery ports should also be configured if possible.
Docker Compose Options
| Option | Usage | Description |
|---|---|---|
| container_name | "jellyfin" | The name of your Docker container. |
| image | ghcr.io/jellyfin/jellyfin:latest | The Docker image to use for the container. |
| user | 'UID:GID' | The user:group IDs of the user that will run the container. |
| group_add | GID | ID of additional group to add. |
| devices | <host-path>:<container-path> | Devices (ex. GPU) to pass into the container. |
| environment | TZ=<timezone-name> | Environment variables that affect the container. You can set variables here such as TZ for declaring a time zone. See more environment configs here. |
| network_mode | bridge, host | Network mode to use for the container. If set to host, remove your forwarded ports. |
| ports | host-port:container-port | Forward the host port to the container port. Refer to the TrueNAS default port list for a list of assigned port numbers. |
| cpus | '#' | Assign # amount of CPU threads to the container. You can't assign more threads than there exists on the installed CPU. |
| mem_limit | #G | Limit memory usage by the container. Can also specify different units: K=KB, M=MB, G=GB |
| restart | no, always, failure, unless-stopped | Declare how to handle automatic container restarts. |
| volumes | /mnt/tank/jellyfin/my-config-dataset:/config:rw | Host mount paths on the host system onto the container |
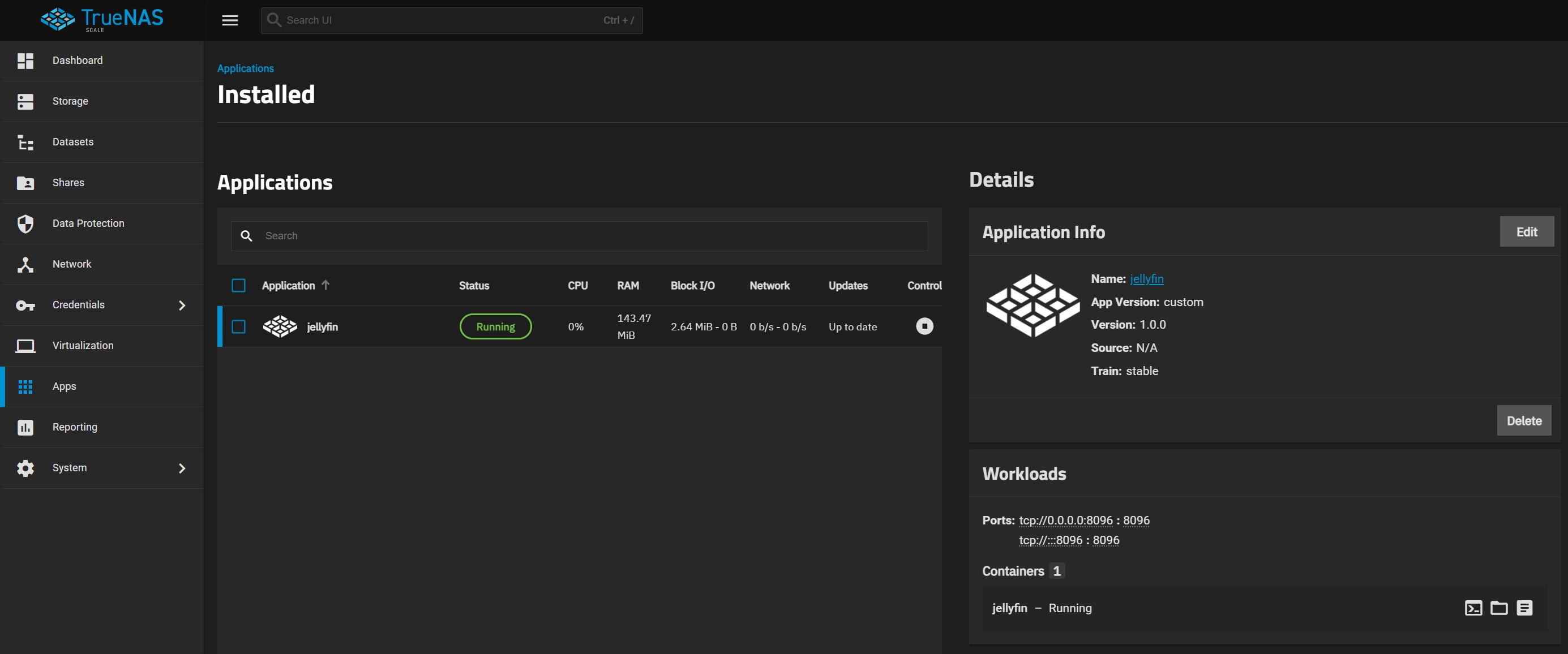
Once installed, you'll be taken back to the main application screen. Here, you can see the status of your Jellyfin container, as well as edit the existing compose file you used to launch it to add more to the container.
- TrueNAS SCALE's YAML interface will re-arrange and remove any comments on your YAML file.
Once the status icon of your Jellyfin container turns to the green Running icon on the UI, your Jellyfin server is up and running.
You can now reach your Jellyfin server by going to a web browser on your local network and using your SCALE server's IP address along the port number you set for Jellyfin (default HTTP port is 8096).
If you used the previous example compose file and your server's IP address is 192.168.1.10, you would use this URL on a browser: http://192.168.1.10:8096
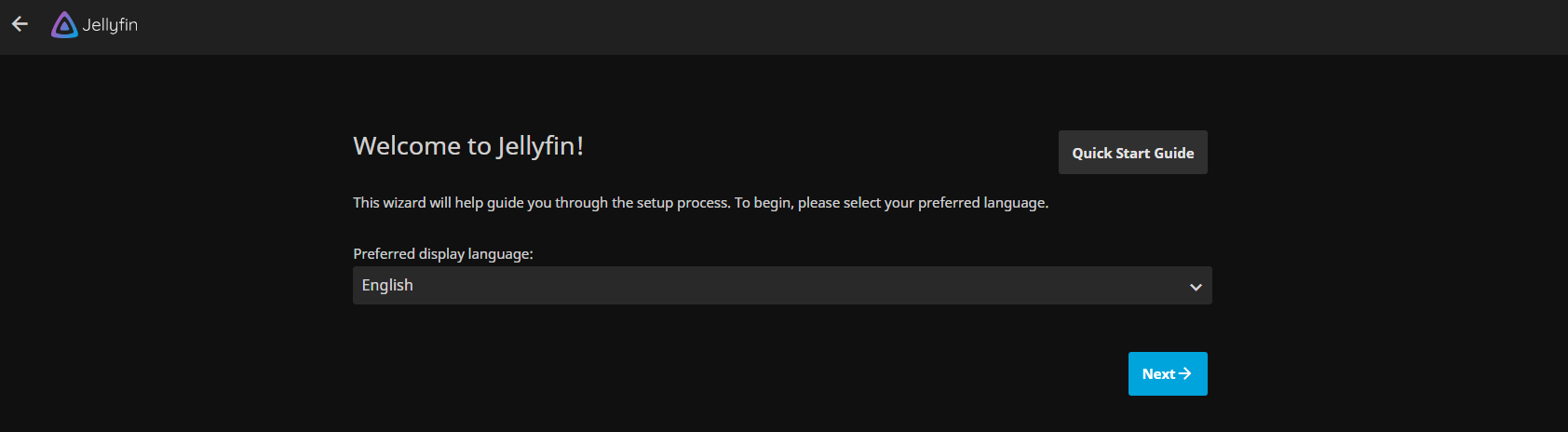
Once you navigate to your server on a web browser, you're now in your Jellyfin server. Proceed with the first-time setup wizard to setup your Jellyfin server. You can also refer to the Jellyfin docs for further assistance.
Adding the Jellyfin Logo to Custom Apps
When you install a custom app on SCALE, it will have a generic SCALE icon instead of the app's official logo.
You can add Jellyfin's logo back by doing the following:
- Go to the system shell
- Switch to root access with the following command (to gain access to the Docker App folder):
sudo -i - Navigate to the location app config location. The directory should be under the name you gave the Jellyfin container when editing the YAML file:
cd /mnt/.ix-apps/app_configs/jellyfin/ - Open the metadata.yaml file with VIM to edit it:
vim metadata.yaml - Enter Insert Mode by typing
i, then go to the end ofhost_mounts: []and hit theENTERkey to make a new line. - Add enough (two) spaces to get the text cursor in-line with the metadata options. Write or paste this new line there:
icon: https://media.sys.truenas.net/apps/jellyfin/icons/icon.svg - Press
ESCto exit Insert Mode, then type:wqand hitENTERto save & quit.
- Notes:
- You can paste to the SCALE Shell using
SHIFT + INSERT - You can force quit without saving in vim by hitting
ESC, then typing:q!
- You can paste to the SCALE Shell using
The file should now look like this:
custom_app: true
human_version: 1.0.0_custom
metadata:
app_version: custom
capabilities: []
description: This is a custom app where user can use his/her own docker compose
file for deploying services
home: ''
host_mounts: []
icon: https://media.sys.truenas.net/apps/jellyfin/icons/icon.svg
maintainers: []
name: custom-app
run_as_context: []
sources: []
title: Custom App
train: stable
version: 1.0.0
migrated: false
notes: null
portals: {}
version: 1.0.0
After this, just go to the custom app in the Apps page. Open the Edit option in Application Info, then click on Save at the bottom. This will update the custom app's icon with Jellyfin's logo.
Installing with the SCALE Community App
To install the Jellyfin application, go to Apps, click Discover Apps, either begin typing Jellyfin into the search field or scroll down to locate the Jellyfin application widget. You might need to click "Refresh Catalog" if no Jellyfin app is showing in the results.
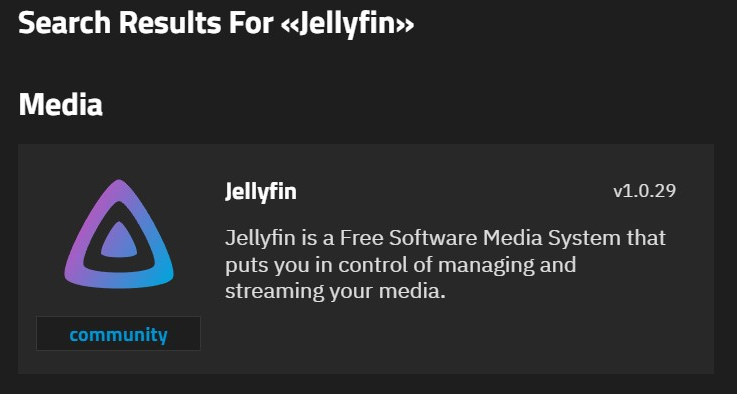
Click on the widget to open the Jellyfin application details screen.
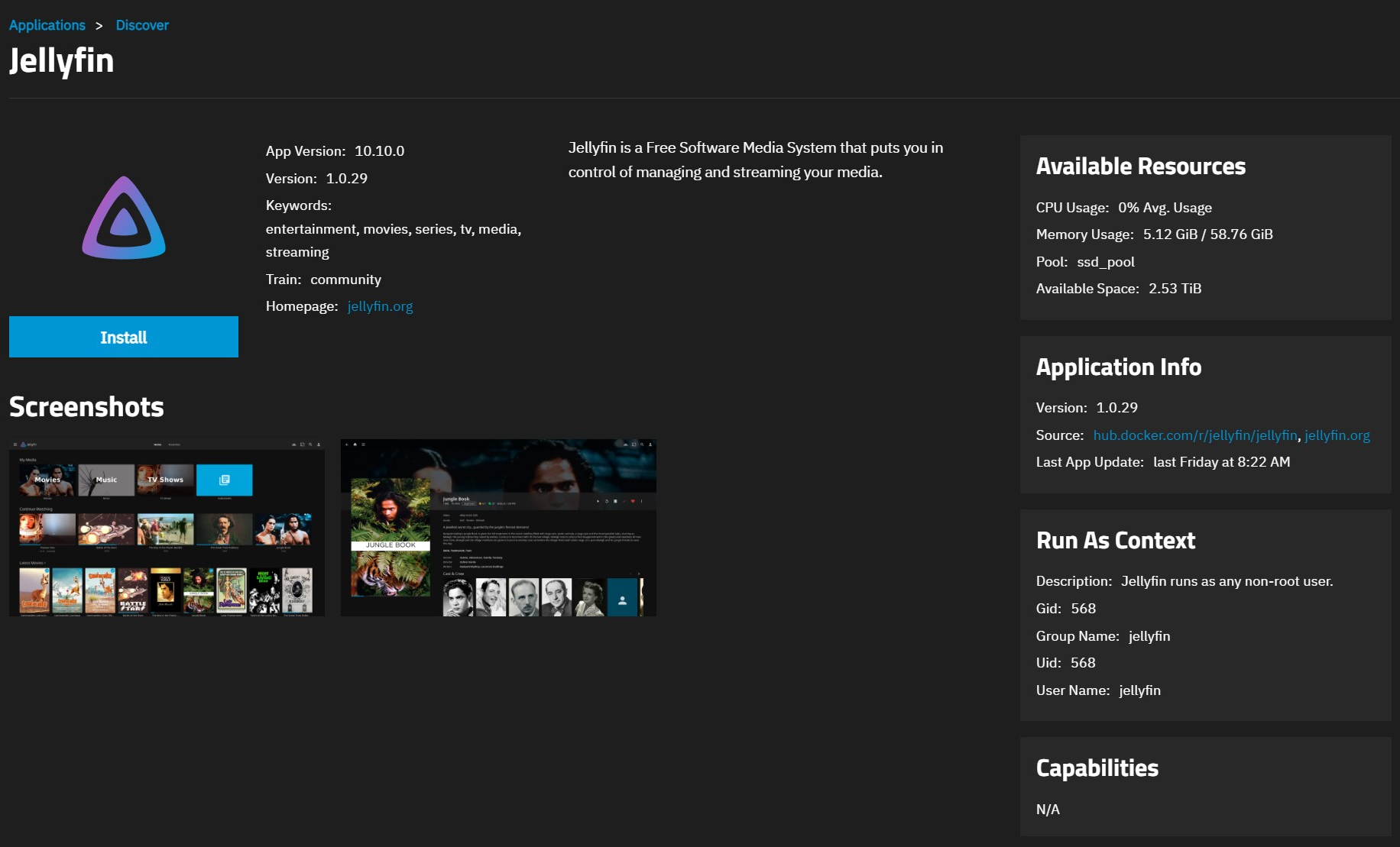
Click Install to open the Jellyfin application configuration screen.
Application configuration settings are presented in several sections, each explained below. To find specific fields, click in the Search Input Fields search field, scroll down to a particular section or click on the section heading on the navigation area in the upper-right corner.
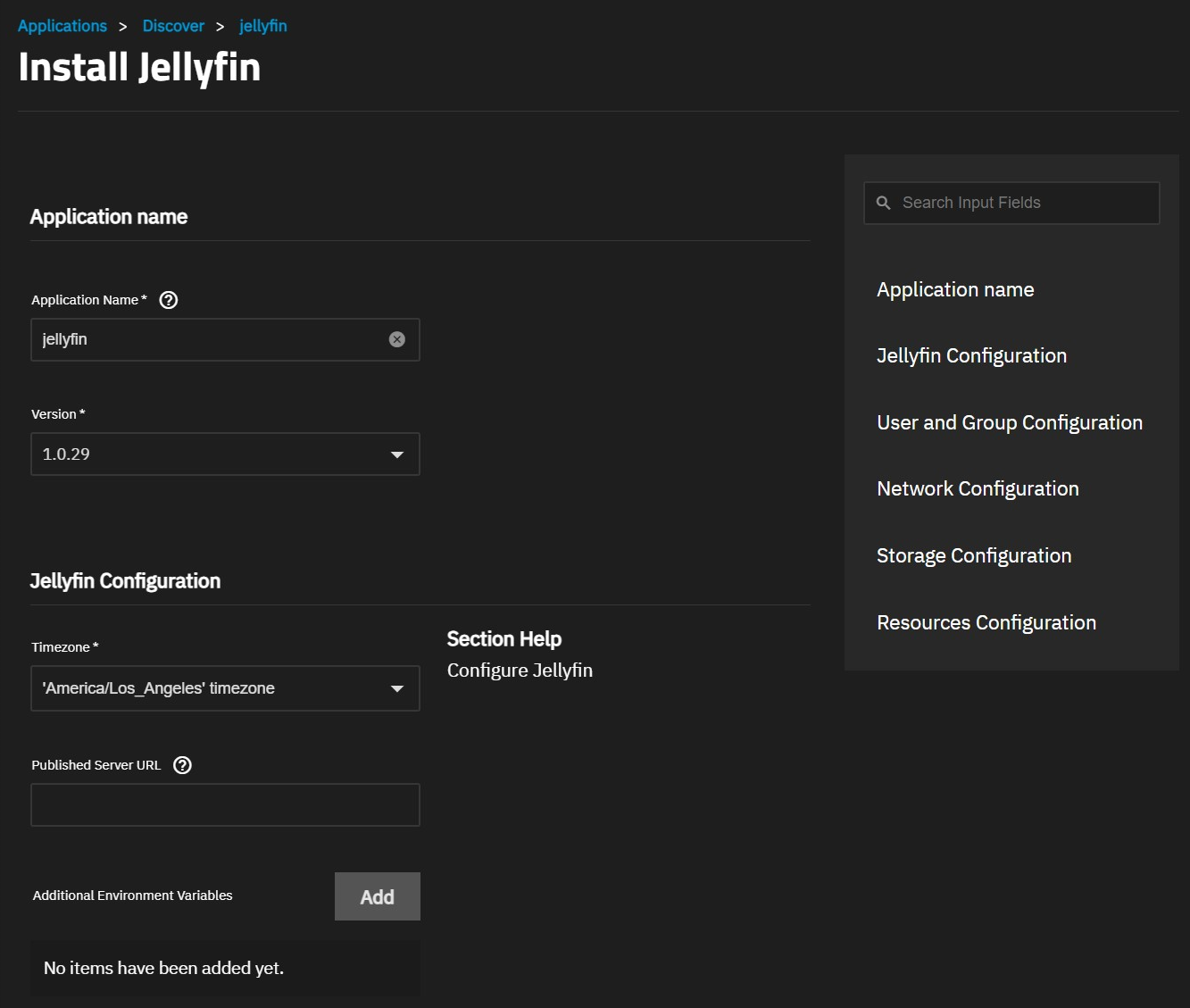
Application Name Settings
Accept the default value or enter a name in the Application Name field. In most cases, use the default name, but if adding a second deployment of the application you must change this name.
Accept the default version number in Version. When a new version becomes available, the application has an update badge. The Installed Applications screen shows the option to update applications.
Jellyfin Configuration Settings
You can accept the defaults in the Jellyfin Configuration settings, or enter the settings you want to use.
You can enter a Published Server URL for use in UDP autodiscovery, or leave it blank.
If needed, click Add to define Additional Environment Variables, see Configuration for options.
User and Group Settings
You can accept the default value of 568 (apps) in User ID and Group ID or define your own.
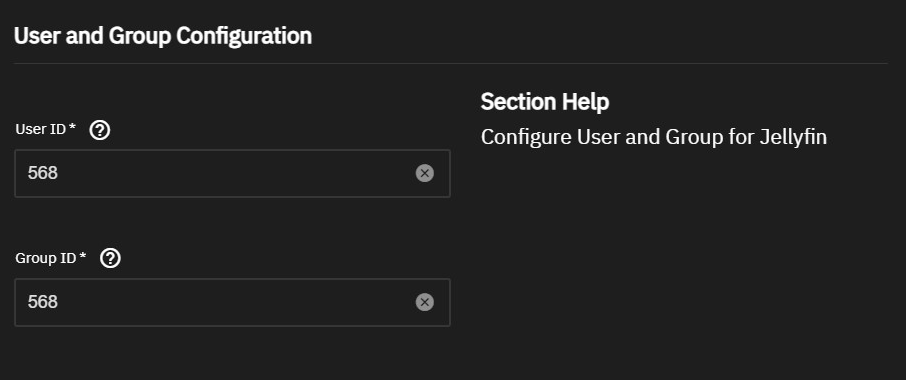
This user and group is used for running the Jellyfin container only and cannot be used to log in to the Jellyfin web interface. Create an admin user in the Jellyfin initial setup wizard to access the UI.
Networking Settings
Select Host Network under Network Configuration if using DLNA, to bind network configuration to the host network settings. Otherwise, leave Host Network unselected.
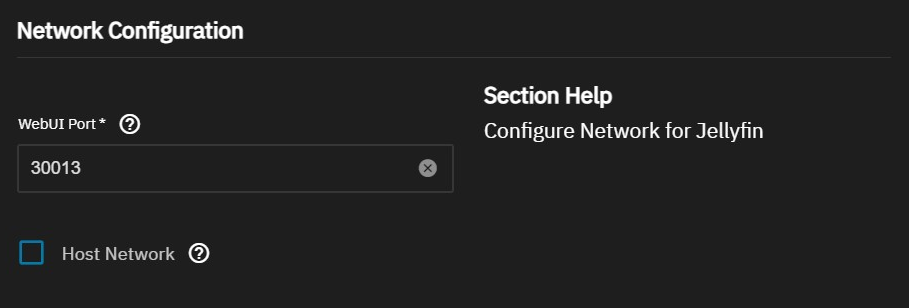
You can accept the default port number in WebUI Port, which is 30013.
You can change this to port 8096. Most Jellyfin clients have built-in scanning features that look for port 8096 by default.
Refer to the TrueNAS default port list for a list of assigned port numbers.
Storage Settings
Jellyfin requires three app storage datasets for:
- Jellyfin Config Storage
- Jellyfin Cache Storage
- Jellyfin Transcodes Storage
Solid state storage is recommended for config, cache, and transcode storage. Do not use datasets located on spinning disks where your media storage/libraries are found for these datasets to avoid slowdowns.
You can install Jellyfin using the default setting ixVolume (dataset created automatically by the system) or use the host path option with datasets created before installing the app.
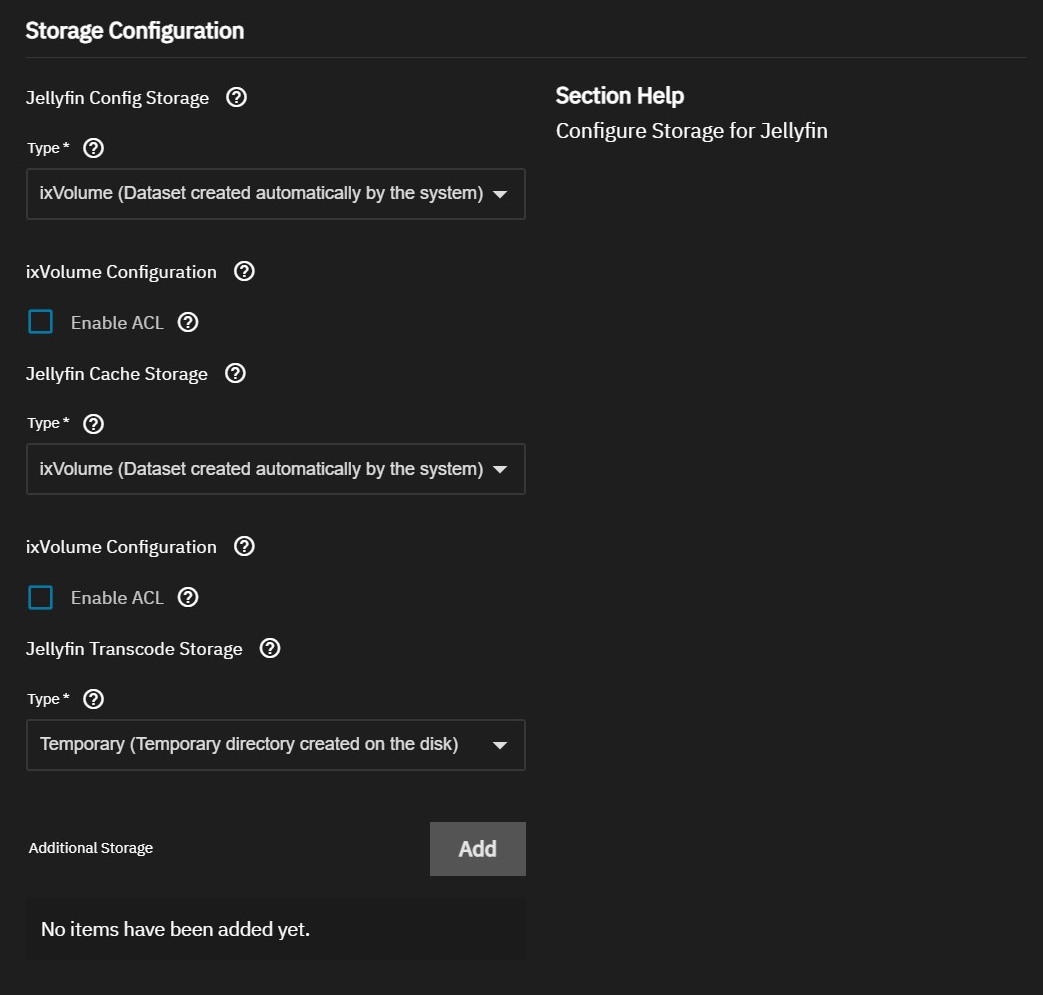
Select Host Path (Path that already exists on the system) to browse to and select the datasets.
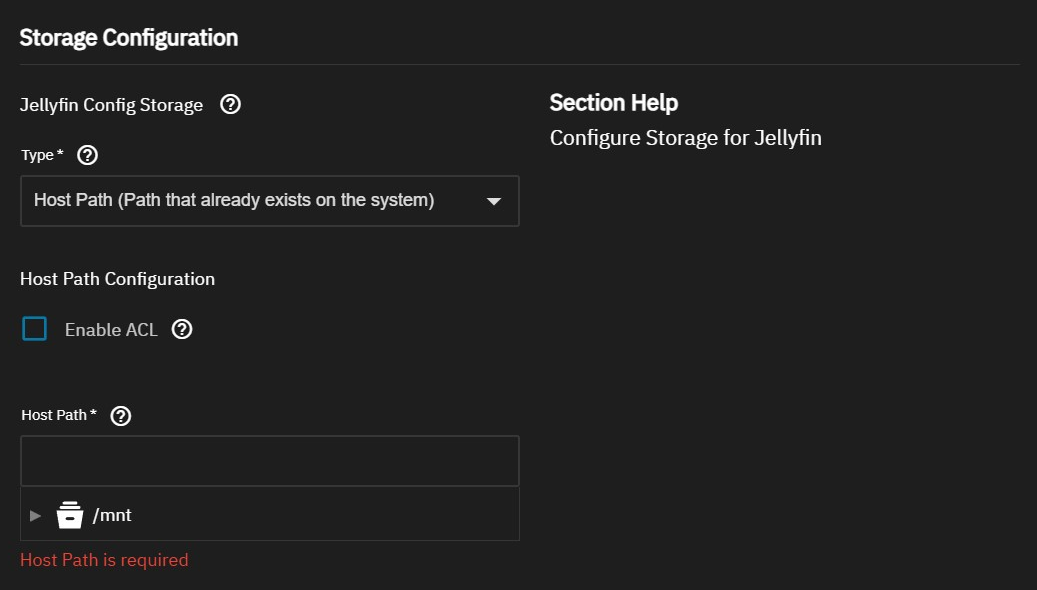
For Jellyfin Transcodes Storage, in Type, select:
- Host Path (Path that already exists on the system) to use an existing dataset created on the system
- ixVolume (dataset created automatically by the system) to let SCALE create the dataset
- Temporary (Temporary directory created on the disk) to use a temporary storage directory created somewhere on the storage pool you set for the Apps system
- tmpfs (Temporary directory created on the RAM) to use a temporary storage directory created on the system RAM
It is recommended to link the transcode directory to a location with decent amount of available storage. Transcodes can take up a lot of space depending on the type of content that is being transcoded. If there's not enough storage here, you will run into playback issues when a transcode doesn't have space to continue being written out.
Mounting Additional Storage
Click Add next to Additional Storage to add the media library storage path(s) on your system.
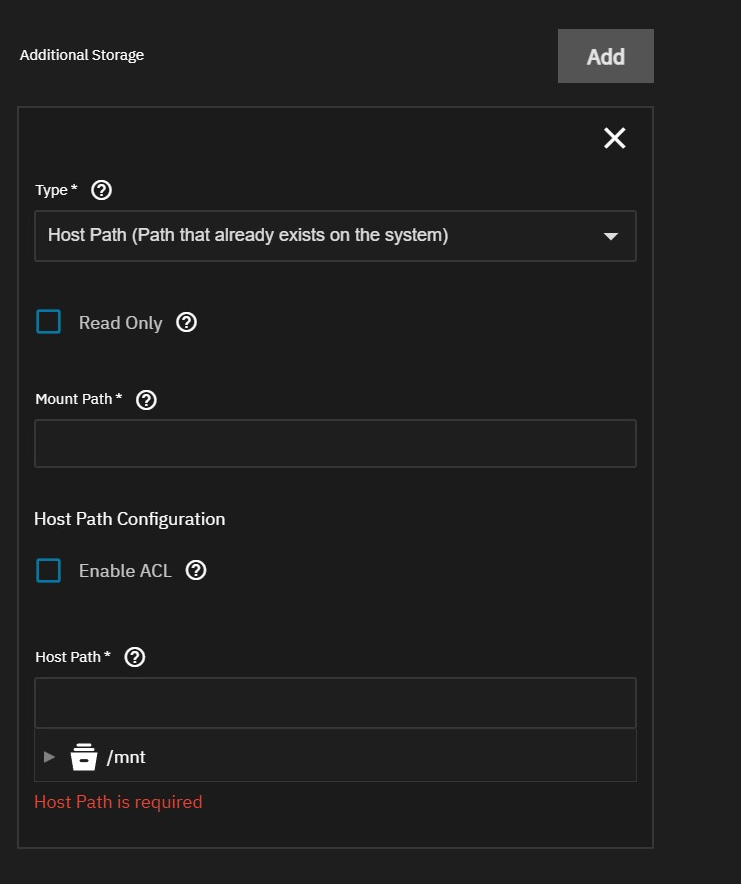
Select Host Path (Path that already exists on the system) or SMB/CIFS Share (Mounts a volume to a SMB share) in Type. You can select iXvolume (Dataset created automatically by the system) to create a new library dataset, but this is not recommended.
Mounting an SMB share allows data synchronization between the share and the app. The SMB share mount does not include ACL protections at this time. Permissions are currently limited to the permissions of the user that mounted the share. Alternate data streams (metadata), finder colors tags, previews, resource forks, and MacOS metadata are stripped from the share along with filesystem permissions, but this functionality is undergoing active development and implementation planned for a future TrueNAS SCALE release.
- Note that if you want to take advantage of Jellyfin's built-in feature of real-time media scanning, you need to mount your media directly with a Host Path as SMB connections do not support this feature.
For all types, enter a Mount Path to be used within the Jellyfin container.
- For example, the local Host Path /mnt/tank/video/movies could be assigned the Mount Path /media/movies.
- With this example, you would browse to
/media/moviesin Jellyfin to see the contents of/mnt/tank/video/movieson your SCALE server.
- With this example, you would browse to
Additional Storage Fields
| Type | Field | Description |
|---|---|---|
| All | Mount Path | The virtual path to mount the storage within the container. |
| Host Path | Host Path | The local path to an existing dataset on the System. |
| ixVolume | Dataset Name | The name for the dataset the system creates. |
| SMB Share | Server | The server for the SMB share. |
| SMB Share | Share | The name of the share. |
| SMB Share | Domain (Optional) | The domain for the SMB share. |
| SMB Share | Username | The user name used to access the SMB share. |
| SMB Share | Password | The password for the SMB share user. |
| SMB Share | Size (in Gi) | The quota size for the share volume. You can edit the size after deploying the application if you need to increase the storage volume capacity for the share. |
Resource Configuration Settings
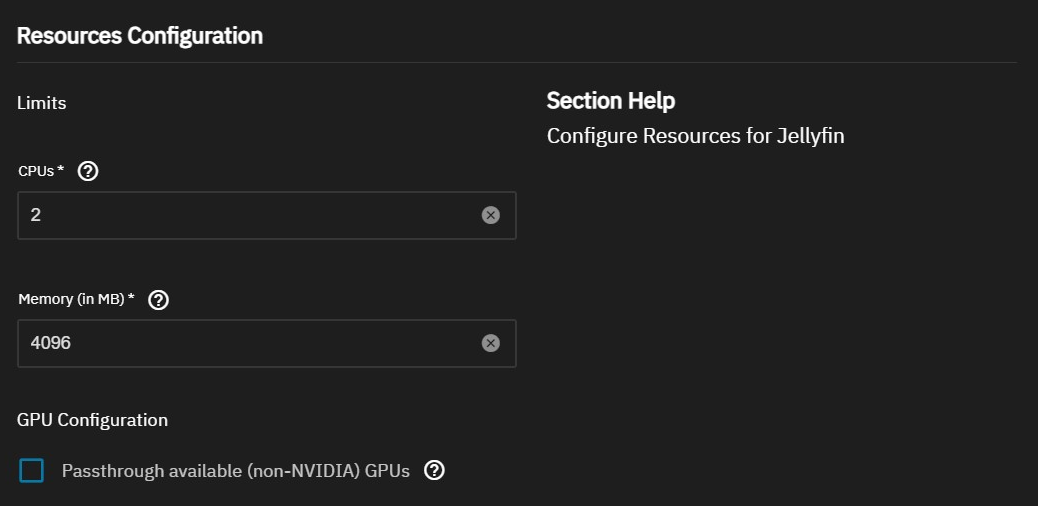
You can customize limits on the CPU and memory allocated to the container Jellyfin will reside in.
- CPUs expects a value in number of threads to assign as a max CPU thread limit.
- You should set this option to the number of threads your CPU contains.
- Refer here for reasonable CPU limits based on your SCALE server's CPU
- Memory (in MB) expects a value in megabytes.
- The default is 4096 which means the container will be limited to 4GB of RAM usage.
- To calculate a value in gigabytes, use this formula where X is a number in MB:
X * 1024 - Refer here for sensible RAM limits for your Jellyfin server
- The max limit you can assign to either limit depends on your SCALE server's specs.
For the GPU Configuration, check the Passthrough available (non-NVIDIA) GPUs option if you need to pass a GPU device for hardware acceleration use with Jellyfin.
- If you have an NVIDIA GPU, please read this.
Finalizing Install
Click Install.
A container launches with root privileges to apply the correct permissions to the Jellyfin directories. Afterward, the Jellyfin container runs as a non-root user (default: 568). Configured storage directory ownership is changed if the parent directory does not match the configured user.
The system opens the Installed Applications screen with the Jellyfin app in the Deploying state. When the installation completes, it changes to Running.
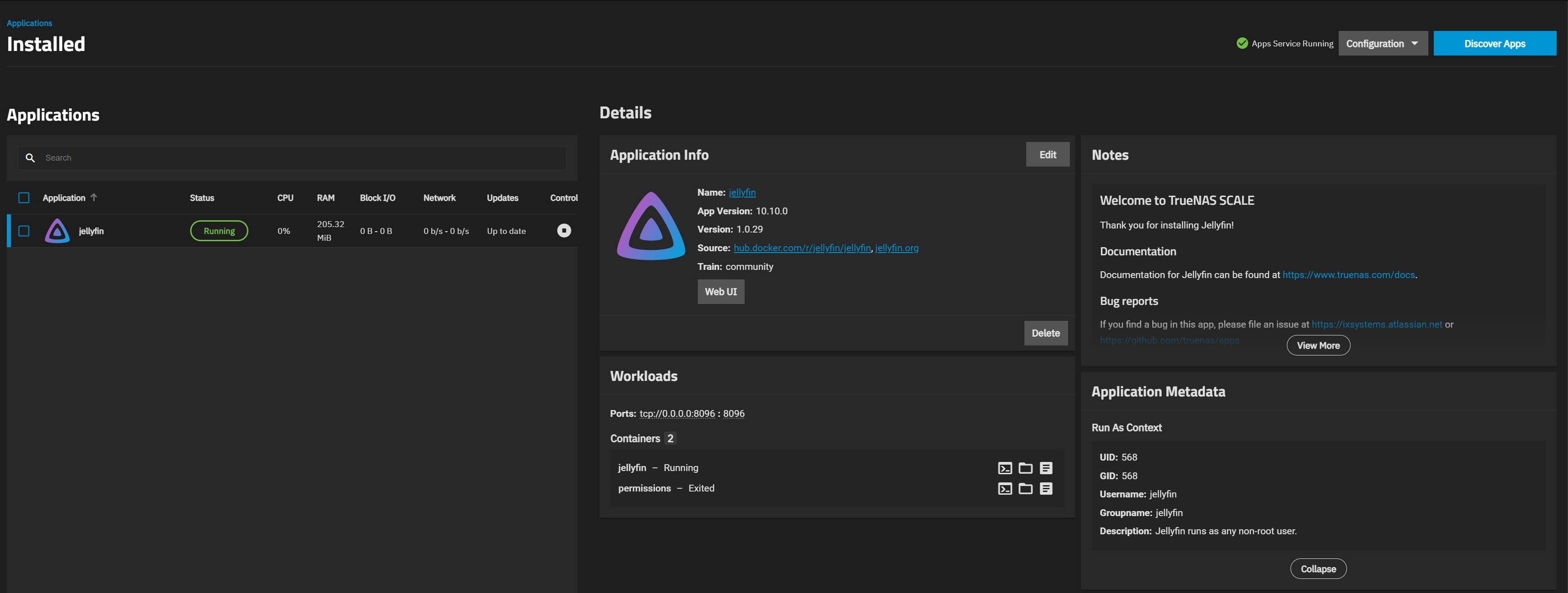
Click the Web UI button on the Application Info widget to open the Jellyfin web initial setup wizard to set up your admin account and begin administering libraries.

Editing the Jellyfin Application
Go to the Installed Applications screen and select Jellyfin from the list of installed applications. Click Edit on the Application Info widget to open the Edit Jellyfin screen. The settings on the edit screen are the same as on the install screen.
- You cannot edit Storage Configuration paths after the initial app install if they have been automatically created by the system (ixVolume).
- You can still modify existing Host Paths storage mounts and paths.
Click Update to save changes. TrueNAS automatically updates, recreates, and redeploys the Jellyfin container with the updated environment variables.
Volume Mount Info & Real-Time Jellyfin Logs
You can access Jellyfin's real-time logs by going to the Workloads widget and clicking on the logs icon on the bottom-right.
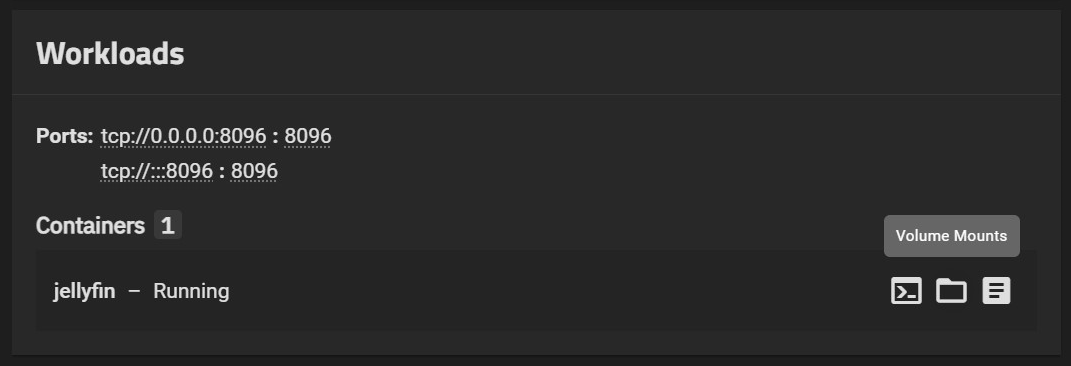
If you didn't specify an external location to mount your config & cache directories, they will be automatically created somewhere on your system. To see the current location of these (and other mounts to the container), click the folder icon on the bottom-right as well in the Workloads widget.
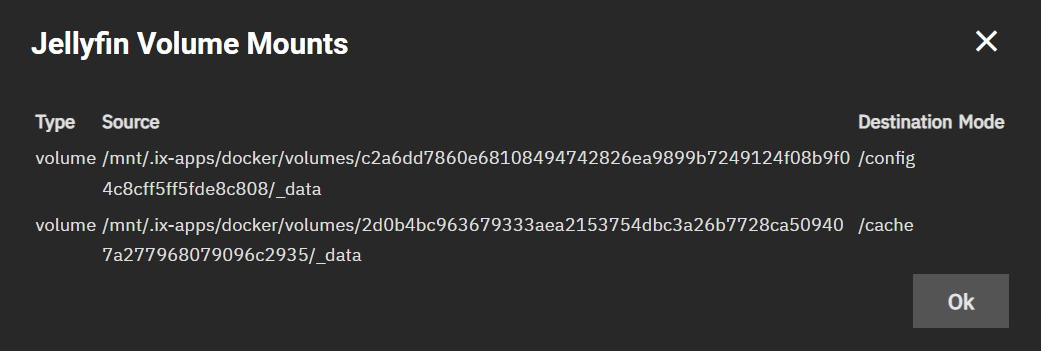
Once opened, you will see a list of all mounts and their paths. You can use this info to navigate to them on your system shell. Note that you will need root (sudo) access to reach Docker-related directories on SCALE.
Managing Container Images
If you want to see the exact images installed on your TrueNAS SCALE server, go to the main Apps page, then click on the Configuration button.
On the dropdown menu, click on Manage Container Images.
You will be brought to a new page where you will see a list of all installed Docker images.
You can also pull new images to use in the future.
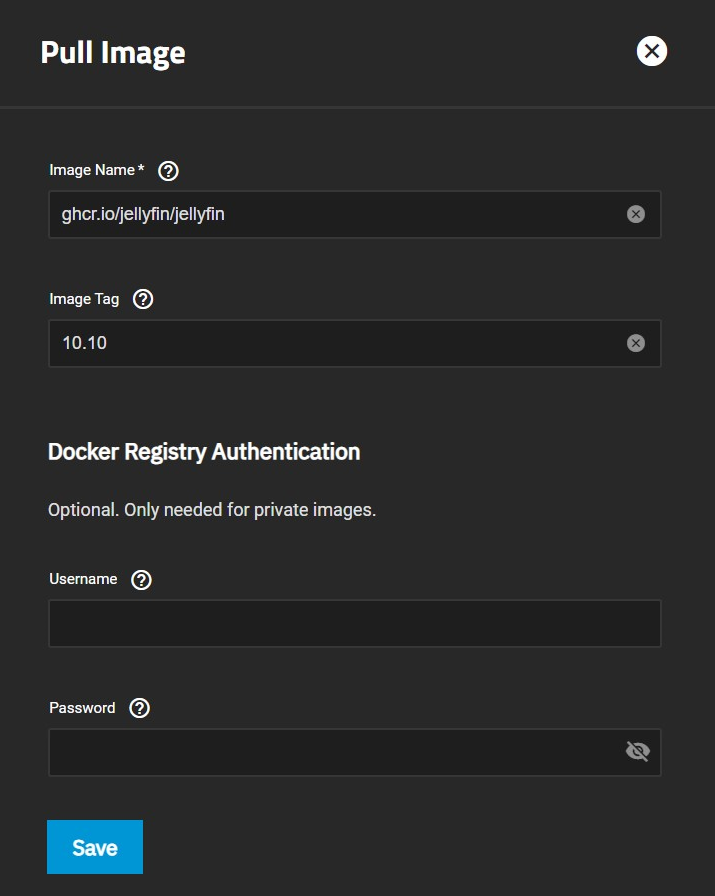
You can choose to pull from Jellyfin's Docker Hub or GitHub Container Registry.
- To pull from Docker Hub, use:
jellyfin/jellyin - To pull from from GHCR, use:
ghcr.io/jellyfin/jellyfin - You can check this blog post for more info about GHCR:
- "Docker users: We now offer GitHub Container Registry (GHCR) as an alternative container registry in addition to Docker Hub. You can pull images from the new registry via URIs like
ghcr.io/jellyfin/jellyfin:latest. Don't worry, we have no plans to drop Docker Hub as a container registry, but we feel providing both gives users more choice and flexibility."
- "Docker users: We now offer GitHub Container Registry (GHCR) as an alternative container registry in addition to Docker Hub. You can pull images from the new registry via URIs like
- Also check out this forum post about how Docker image tags can be used.
If you have a container using any of your images, SCALE should notify you of an available update to the image through its GUI provided you used the latest tag, or one of the other tags that doesn't point to a single release.
NVIDIA GPUs on SCALE (v24.10+)
- For users with an NVIDIA GPU, read the v24.10 Electric Eel release notes regarding your GPU:
"Starting in 24.10, TrueNAS does not include a default NVIDIA GPU driver and instead provides a simple NVIDIA driver download option in the web interface. This allows for driver updates between TrueNAS release versions.""Users can enable driver installation from the Installed applications screen. Click Configure > Settings and select Install NVIDIA Drivers. This option is only available for users with a compatible NVIDIA GPU and no drivers installed or for users who have previously enabled the setting."